Traumatic brain injury

CAUSES OF TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY:
Injury from outside the head, in which a force is exerted on the head, it may have damaged the skull.
Injury with 'external' objects penetrating the brains. A penetrating head injury, or open head injury, is a head injury in which the dura mater, the outer layer of the meninges, is penetrated. Penetrating injuries can be caused by high-velocity projectiles or objects of lower velocity, such as knives, or bone fragments from a skull fracture that are driven into the brain.
Several causes of traumatic brain injury may be by force on the head;
Beaten or kicked on the head
Being struck
Fall to the ground
Getting an object on the head
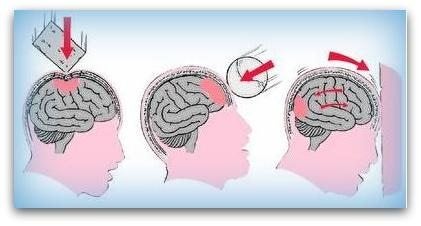
Possible causes of injury in which external objects penetrate the brains;
A bone portion that enters the brains as a result of a skull fracture.
An object that enters the brains. Think of a bullet, piece of shrapnel, stabbing weapon, iron object from an accident.
In such cases, the cause of the injury is not the increase of the pressure on the brains, but the object which directly damages the brains.
In most cases, traumatic brain injury occurs when the head suddenly slows down or speeds up. See picture below: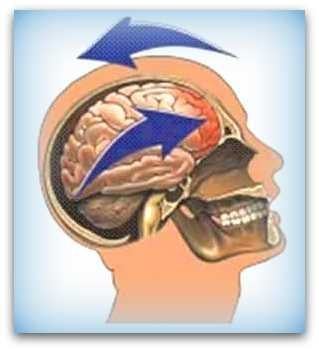
SYMPTOMS
TBIs can cause many symptoms, depending on their severity and which part of the brain they affect. Among possible symptoms are:
- Loss of consciousness
- Headache
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Memory problems
- Trouble thinking
- Mood changes
- Personality changes
- Nausea or vomiting
- Agitation
- Seizures
- Change in sleep patterns
- Difficulty waking up
- Problems with coordination
- Weakness or numbness in the arms or legs
CONTUSION, CONCUSSION OR WHIPLASH?
- Brain contusion (cerebral contusion or contusio cerebri in Latin) shows at least a period of unconsciousness of 15 minutes and longer, or a period of PTA, longer than 60 minute ('hole' in the memory)
- Sequelae after concussion (post commotion syndrome PCS or PPCS) brief period of unconsciousness in concussion, sometimes even without unconsciousness
- Whiplash, this has not made the person unconscious, just 'out'
WHAT IS A BRAIN CONTUSION?
A brain contusion is severe traumatic brain injury in which the brain is damaged, unlike a concussion with no or minimal brain damage.
Like bruises in other tissues, cerebral contusion can be associated with multiple microhemorrhages, small blood vessel leaks into brain tissue. Contusion occurs in 20–30% of severe head injuries.
With a brain contusion, there is always loss of consciousness for at least fifteen minutes, and the loss of consciousness is deeper than in case of a concussion.
By the force of the blow or impact to the head, a bruising of the brain tissue is created.
Brain tissue is broken and the brain is oppressed by blood and fluid (swelling).
This means there is extensive and complex damage to the brains. Since cerebral swelling presents a danger to the patient, treatment of cerebral contusion aims to prevent swelling.
Due to the danger of increased intracranial pressure, surgery may be necessary to reduce it. People with cerebral contusion may require intensive care and close monitoring.
Depending on the severity and location of the bruising, effects differ.
One person with cerebral contusion may recover almost completely and the other can keep on suffering from severe disabilities.
Possible sequelae are divided into categories:
- physical problems
- emotional and personality changes
- motoric disorders
- psycho-social problems
- cognition (see list below for cognitive impairment)
After a TBI, neurons (nerve cells) in the brain may be damaged. As a result, the neurons may have trouble doing their job of carrying signals to different parts of the brain. As a result, if you have a brain injury, you could have trouble thinking or moving as you normally do. Your brain may also have trouble keeping your body working properly.
The great need for structure in daily life is striking!
A typical phenomenon associated with brain injury, is the disharmonious profile: for example, a high IQ on the verbal level, but markedly lower at the executive level (such as organizing or perpetrating of acts). The pace of thinking can also be affected.
MILD TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
problems after concussion or whiplash
Most people recover after a concussion or whiplash.
There are still people who suffer cognitive and / or physical problems after a concussion or whiplash
If no damage has been established to the brain and the person continues to have symptoms, it is not always evident that this person suffers from brain injury.
Recently, it was discovered that a circulation problem was detectable in the time shortly after a concussion with a SPECT scan (contrast fluid).
An American study showed 53% of people with long-term post commotioneel syndrome (PCS) or a disturbance in the blood flow in the brains detected. (See research result here..)
However, not many people end up in this medical research circus in the period following a concussion. They have something "else on their minds" ... A study with MRI or CT scan showed that the Spect scan showed more abnormalities in this area than did the MRI or CT scan.
A biomarker (calpain-cleaved αII-spectrin N-terminal fragment (SNTF)) in the blood predicts the risk of white matter lesions and cognitive complaints after mild traumatic brain injury ( See study here..)
Also, a neuropsychological assessment may reveal hidden cognitive damage, but this is very expensive.
If the person in question keeps suffering from various symptoms and is labelled as suffering from "light" or "mild" brain injury, it would certainly be advisable to inquire about a (possibly self-paid) neuropsychological assessment.
Especially when there is nothing to see on MRI or CT scan, someone might perhaps just keep on going on and persevere.
COGNITIVE DISORDERS
Cognitive disorders are related to cognition: thinking, language, memory, concentration, processing knowledge, perception, awareness, and attention. So it is a broad term.
In patients with brain contusion these disorders can express themselves in the following ways:
- Impaired intellectual functioning (sometimes only partial)
- Delays in the processing of information (mental slowness)
- Attention deficits
- Memory problems
- Orientation Issues
- Visual-spatial problems
- Problems with coordinating daily and / or complex actions (apraxia)
- Problems in identifying things or issues
- Language problems
- Problems with calculation
- Problems with executive functions
COUP AND CONTRA COUP
The brains are the most complex and vulnerable part of the human body. It has a composition resembling a gelatin like structure.
By a blow or fall or impact the brains shake back and forth, causing back and front injuries to occur due to the centrifugal force. (Or side and opposite side)
You see in the video below on the side of the blow swelling, bruising and tearing of blood vessels. This is called a 'coup'.
Because the brain moves slower than the skull, the brains first clashes against the bone on the side of the blow.
But then the brains will go against the back of the skull to collide. This is called a "counter-coup."
Also at the back occurs bruising and tearing of blood vessels. Both front and back are now damaged. See videos below:
On a microscopic level, not visible on an MRI scan, the braincel body can tear off from the axons. The axons give signals to the different brain bodies.
After the tear both axons and the brain-body die within seconds. These dead brain cells cannot communicate with each other ...!
In the dying process chemicals are released; neurotransmitters. They provide even more damage. The lesion then spreads in the immediate vicinity of the affected brain cells. That damage can last up to 24 hours after the initial impact. That is why the first 24 hours after the accident are so crucial.
LEFT OR RIGHT DAMAGE?
Roughly you can say that the left-hand side of the brain controls the right-hand side of the body and also the language functions are mostly located in the left-hand side of the brain. The right-hand side controls the left-hand side of the body. Injury on the right-hand side of the brain gives more impulsive, quick-tempered behaviour or spatial insight problems .... Read more
People with brain injuries who look normal may be able to only live a very limited life and they may be very easily overwhelmed and tend to be overestimated by their environment, precisely because there is nothing to see on the outside. Even an MRI may not reveal any damage; but the injuries can have very serious consequences in life. Mutual brain connections may have totally disappeared.
LIST OF COMPLAINTS AFTER brain contusion
The brain contusion CCF Foundation has published the list below.
"Top 14 of complaints as reported by contusiopatients, 12 months after the accident, with decrease of Trauma Complaints List (Of Zomeren and Van den Burg, 1985). Frequencies are percentages of affirmative answers. Notice that headache, contrary to what you might expect, is not the most frequently given answer."
49% forgetfulness
41% increased fatigability
39% increased need for sleep
36% irritability
34% of inertia
31% concentration
30% sensitivity for crowds
27.5% dizziness
26% sensitivity to noise
25.5% loss of initiative
25.5% headache
21% easily overwhelmed by emotions
21% inability to do two things at once
19% depressed mood
POST TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER/ PTSD
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a severe stress reaction to a shocking event. It is also a natural reaction to an unnatural event.
There is a chance that someone with the rise of traumatic brain injury also develops PTSD, as the cause of the brain injury was a very shocking event. For example in:
- natural disasters
- aircraft accidents or serious car accidents
- terrorist attacks
- assault with violence causing brain injury
- rape by force, causing brain damage
- robbery with violence, causing brain damage
- confrontation with someone who is seriously injured or slain and spearheading this experience
- war experiences
Post-traumatic stress disorder has the following characteristics:
Extreme loss of control. People are losing their grip on daily life. Many victims feel powerless.
Disruption: Obvious expectations no longer apply. Confidence in themselves, other people and everyday life is gone. One is faced with his own vulnerability.
Such a shocking event may cause a disruption of the psychobiological balance. People remain set at danger. The fear is permanent. This condition disrupts their daily lives, with the possible consequences:
- Chronic stress
- Excessive vigilance
- Physical complaints
- Reliving of the trauma
- Nightmares / Night Terrors
- Fears
This situation needs to be treated by experienced neuro-psychologists who have knowledge of both brain disorders and PTSD.
It may also be necessary to refer to (neuro)psychiatrists.
Links
Car accidents and Brain Injury statistics
Resources hersenstichting.nl, hersenletsel-uitleg.nl, neurological aspects of long term outcome prognosis in pediatric closed head injuries Ruijs, hersenkneuzing.nl, Coping with brain injury Palm, Frontiers in neuroloy, neurotrauma, brain health board in boxers and soccer, Left brain right brain Springer & Deutsch, JBM Kuks, J. W. Pike, H.J.G.H. Oosterhuis. Clinical Neurology 15th Edition, Bohn Stafleu Of Loghum, Wood, 2003, ISBN 90-313-4028-6 Columbia University Neurosurgeons http://www.columbianeurosurgery.org/conditions/traumatic-brain-injurytbi/ Gennarelli GA, Graham DI (2005). "Neuropathology". In Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC. Textbook Of Traumatic Brain Injury. Washington, DC: