Hypothalamus
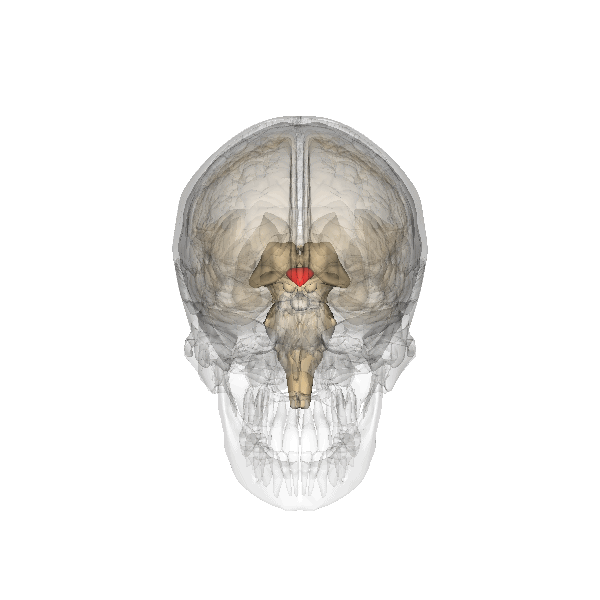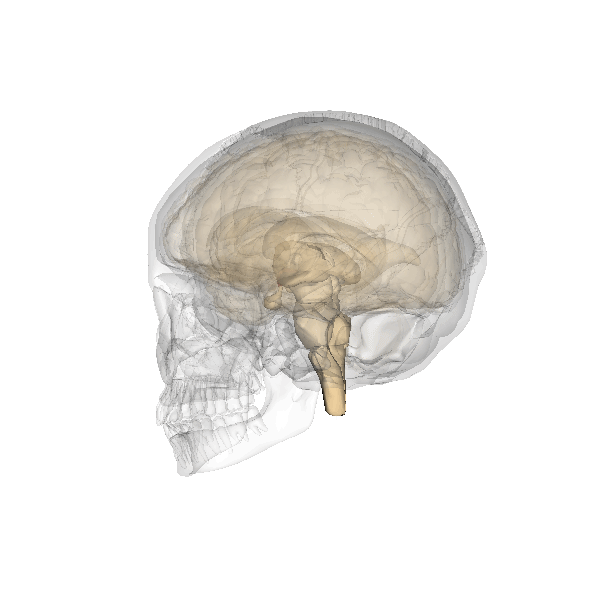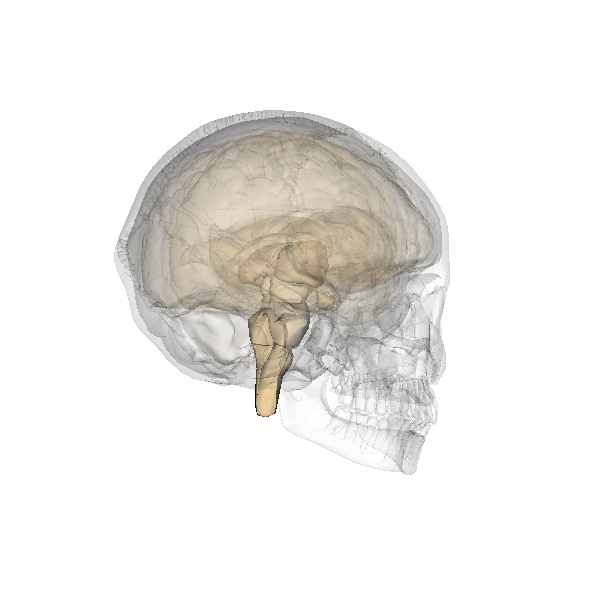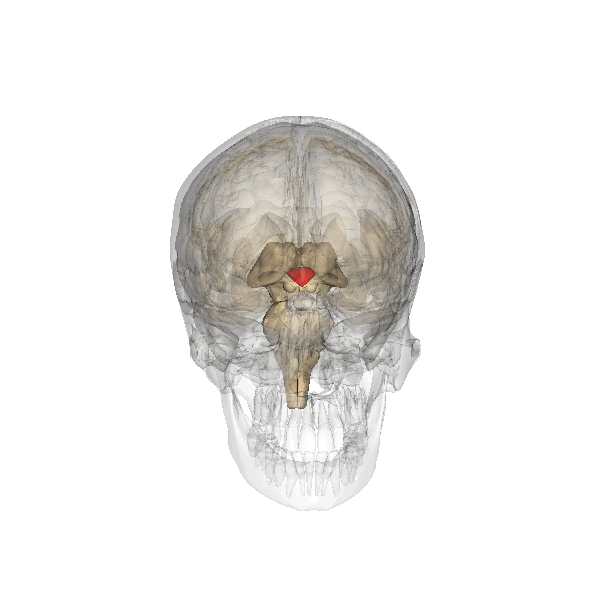
The hypothalamus (in the drawing: the red small triangle) is located diagonally above the thalamus. It is also located just above where the optic nerves cross. It is part of the intermediate brains, the limbic system. The limbic system has to do with emotion, delight, motivation and emotional memory.
(Researchers discover more and more areas of the brain that deal with emotion)
The hypothalamus has several functions including the control of the endocrine system. The hypothalamus can release hormones itself and can control the pituitary gland which in turn produces hormones.
But also the hypothalamus regulates the autonomic nervous system, among others with breathing, heartbeat, blood pressure, and to control the body temperature.
It prepares the body for action and contributes to the recovery of the body at rest. But also hunger and thirst feelings and feeling of saturation are regulated here, but also sexual arousal and sleep-wake schedule are settled here.
Damage in the hypothalamus can result in the following symptoms
(NB! each injury and each human being is different):
- lack of motivation
- lack of appetite or thirst with the result that the person eats/drinks too little
- excessive hunger or feeling of thirst with the result that the person eats or drinks too much
- rapid digestion
- changed libido
- changed sleep-wake schedule, sleepiness
- altered menstrual pattern
- feelings of euphoria
- hyperactivity
This page is approved and monitored by P.A.W.Frima-Verhoeven, Neurologist Recuper 2015
Resources:
hypothalamus. Images are from Anatomography maintained by Life Science Databases(LSDB). 日本語: 視床下部。
circuit van papez, http://www.brainmatters.nl/terms/limbisch-systeem/ Bart Aben, brainmatters
http://wetenschap.infonu.nl/anatomie/124575-hormonen-van-de-hypothalamus-en-hypofyse.html
https://www.hersenstichting.nl/alles-over-hersenen/de-hersenen/anatomie/hypothalamus