Frontal lobes
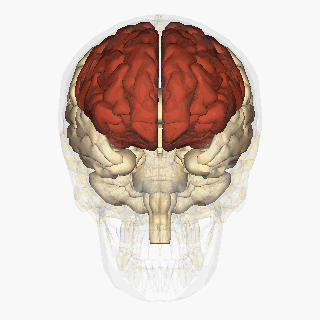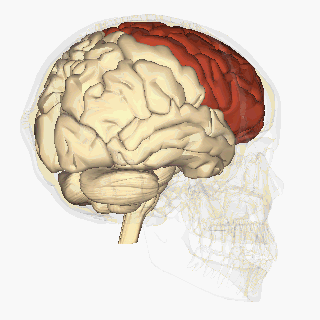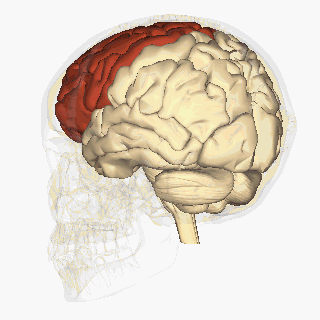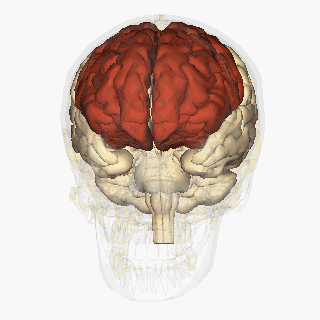

The frontal lobes are located behind the forehead.
They are the largest lobes of the brain and they are extremely vulnerable to injury due to the fact that they are located at the front of the cranium and because of being near rough boney ridges, (proximity to the sphenoid wing) and their large size.
They are involved in:
- Planning
- Organizing
- Memory
- Impulse control
- problem solving
- Selective focus
- Decision making
- The control of behavior and emotions
The left frontal lobe also plays a role in speech and language.
Damage to these lobes may affect: emotions, language, impulse control, memory, social- and sexual behavior.
More specific:
- Loss of simple movement of various body parts (Paralysis)
- Inability to plan a sequence of complex movements needed to complete multi-stepped tasks, such as making coffee (Sequencing)
- Loss of spontaneity in interacting with others. Loss of flexibility in thinking
- Persistence of a single thought (Perseveration)
- Inability to focus on task (Attending)
- Mood changes (easily overwhelmed by emotions)
- Changes in social behavior. Changes in personality
- Difficulty with problem solving
- Inability to express language (Broca's Aphasia)
More information about the impact of damage to the frontal lobes you can find on the website of the Centre for Neuroskills.