Impact of brain injury per brain area
Where is the injury? Explained per brain area
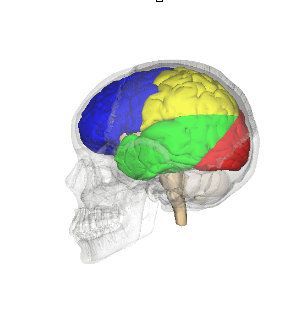
Learn more about particular damage in these areas:
The blue area is the Frontal lobe
The yellow area is the Parietal lobe







Brain structure
CORTEX (cortical) and SUBCORTEX (subcortical)
The outside of the brain is the cerebral cortex or cortex cerebri.
The brain areas that lie underneath are called the subcortical brain areas.

CORTEX
The terms 'cortex cerebri' and 'cortical' refer to important parts and functions of the brain. The cortex cerebri is the outermost layer of the cerebrum and plays a crucial role in higher cognitive functions such as thinking, consciousness, perception, language and memory.
This structure is made up of gray matter, which consists of billions of nerve cells, and is essential in processing complex information. The word "cortical" is an adjective that describes something related to the cerebral cortex. Read more about gray matter and white matter via this link.

SUBCORTEX
The subcortex is an essential part of our brain that is located under the cerebral cortex.
It plays a crucial role in fundamental functions such as emotions, memories, motivation and automatic body processes. This part of the brain contains brain structures such as the thalamus, as a relay for much information, the amygdala, the hippocampus and the basal ganglia, which work together to control behavior, movement and feelings. See image below.
The subcortex often works unconsciously, helping us carry out daily routines without having to actively think about it.

Photo series with explanation
For the photo series below, click on the arrow to the right to see the next photo.























